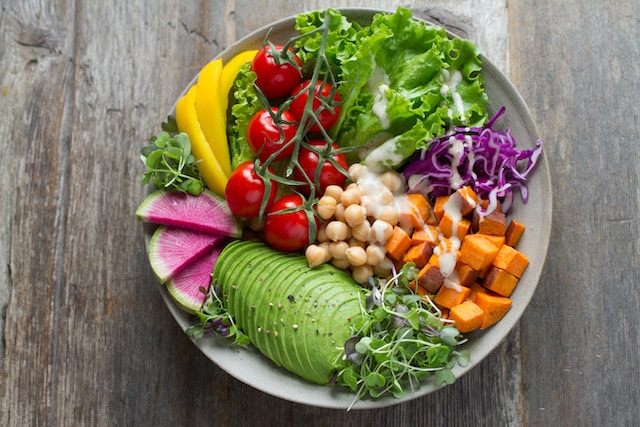
We tend to think of inflammation in an acute sense — the swelling of an ankle after spraining it trying to sink a jump shot, the puffiness in the skin surrounding a bee sting, or the post-surgical inflammation around the incision site. While these are all examples of inflammation, the majority of the inflammatory load we experience is actually on a more low-grade, but chronic level.
Unfortunately, while it might seem innocuous if it goes on mostly undetected, studies show that prolonged inflammation — even low grade — is dangerous and can lead to the development of chronic diseases like heart disease, obesity, Type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and certain autoimmune diseases.
One of the primary sources of chronic inflammation is actually the food we eat. Because the digestive tract serves as the first site of contact between the foods we ingest and our bodies, it is constantly exposed to different toxic compounds in processed foods, making the gut highly susceptible to inflammation.
Because quelling systemic inflammation reduces your risk of various health conditions, increases energy, and improves your mood, skin health, brain function, and overall well-being, we recommend loading your plate with plenty of anti-inflammatory foods. Though many nutritious foods such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and fish can reduce inflammation, we’ve rounded up the best anti-inflammatory foods to add to your diet.

Why the foods we eat matter
Certain foods can either increase or decrease inflammation in the gut and the body in general. Foods that inflame the body trigger a cascade of inflammatory pathways by damaging cell walls and harming the beneficial bacteria in the gut. These bacteria play a key role in producing anti-inflammatory compounds and maintaining the integrity of the gut lining. If your gut flora is compromised, the gut barrier becomes damaged and more permeable.
If a normal gut lining is visualized as a fine sieve, just allowing a few certain things to pass from the gut through the barrier to the bloodstream, a damaged or “leaky gut” is like a colander with big holes that permit the passage of undigested food particles, harmful metabolic byproducts, and gut bacteria themselves to enter circulation. Because these particles don’t belong in the bloodstream, their presence causes the immune system to react, which incites inflammation.
Unlike inflammatory foods, such as sugar-sweetened beverages like soda and juice, red meat, refined grains, fried foods, hydrogenated oils, and alcohol, anti-inflammatory foods support the good bacteria in your gut and may either increase the production of anti-inflammatory compounds or inhibit inflammatory pathways.
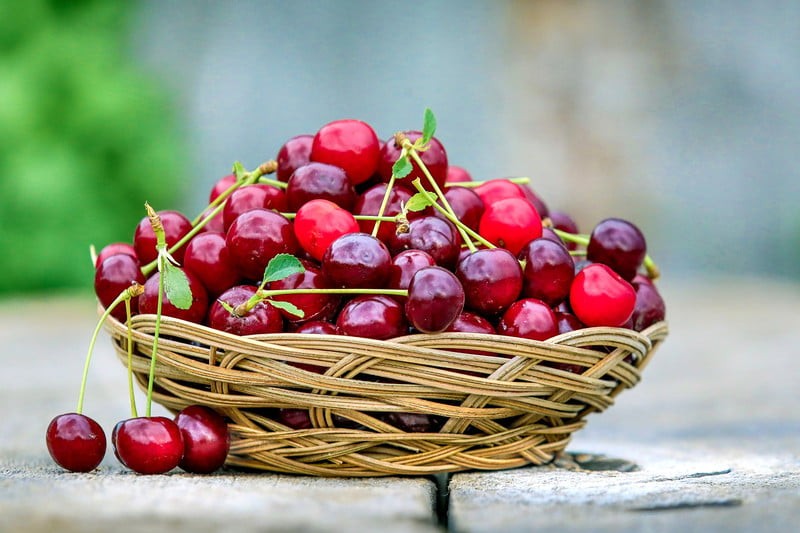

Tart cherries
Numerous studies have demonstrated that tart cherries possess particularly potent anti-inflammatory properties. In fact, tart cherry juice and tart cherry supplements are often recommended for people suffering from arthritis pain, and some studies have found the pain-reducing benefits of tart cherry extract to be comparable to that conferred by ibuprofen and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. Tart cherries are rich in antioxidants, polyphenols, and flavonoids that reduce oxidative damage and inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines.
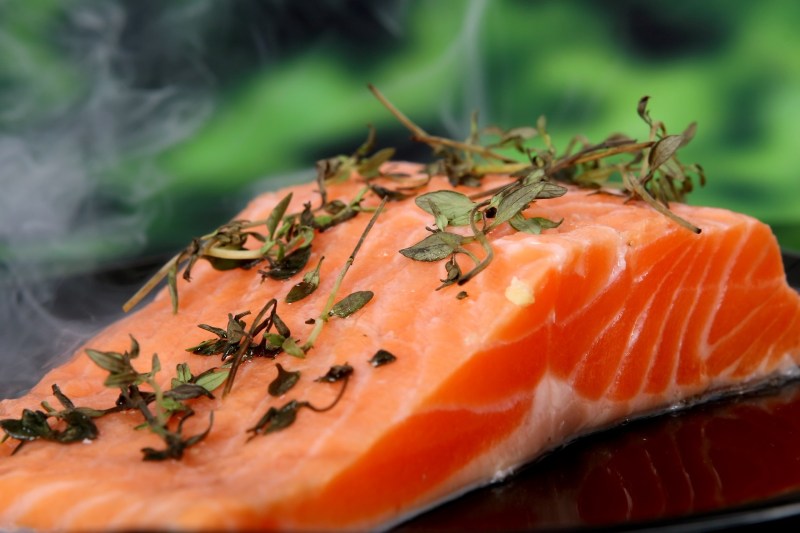

Fatty fish
Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, exert strong anti-inflammatory effects in the body and have been found to improve brain and heart health. Moreover, studies show that increasing the intake of omega-3 fats relative to omega-6 fatty acids helps counter the inflammatory effects of omega-6 fatty acids and hydrogenated oils. Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, mackerel, and tuna are some of the richest sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
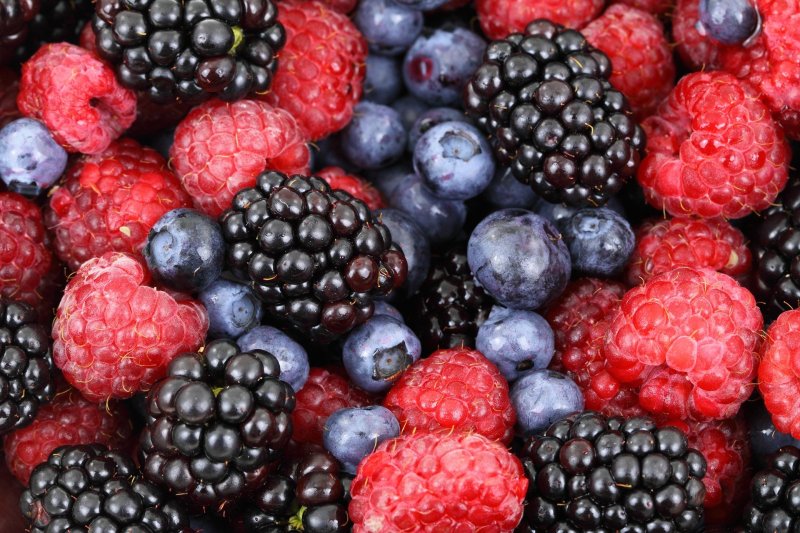

Berries
Raspberries, blueberries, strawberries, blackberries, and boysenberries, are tiny but mighty nutritious powerhouses full of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and polyphenols. Plant compounds, such as polyphenols and other phytonutrients, act as free radical scavengers and can block or protect against oxidative damage from other harmful compounds and toxins in our environment and diets.
They also reduce inflammation and improve insulin sensitivity. These beneficial polyphenols are most of what imparts the various pigments to fruits and vegetables, and the wide range of hues and colors we see in the produce section of the grocery store is indicative of the different phytonutrient profile each fruit or vegetable possesses. Red berries contain a lot of astaxanthin, which inhibits inflammation, and blue and purple berries have anthocyanins, which help the immune system produce natural killer cells.
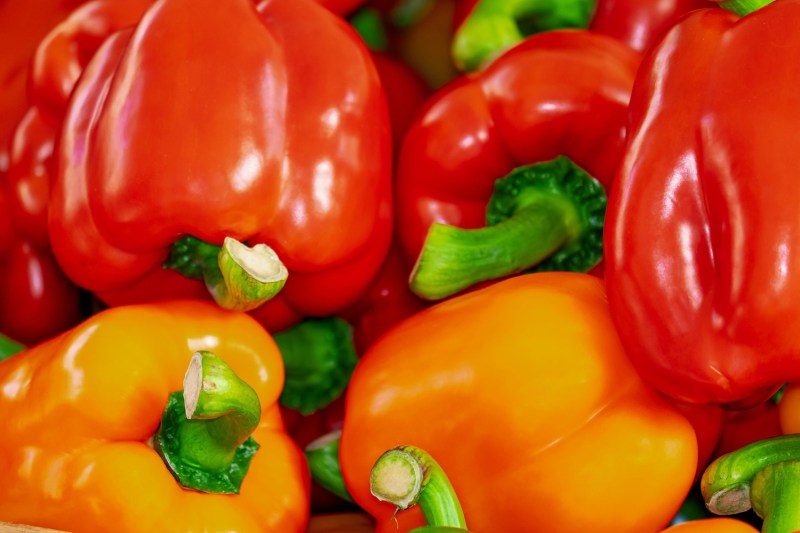

Orange, red, and yellow peppers
Bell peppers are one of the best dietary sources of vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant that increases cell turnover and supports the immune system. Orange, yellow, and red bell peppers are especially nutritious because they also contain vitamin A, beta-carotene, and lycopene, which help regulate inflammation by suppressing pro-inflammatory T-helper cells and suppressing the expression of genes for different inflammatory cytokines.
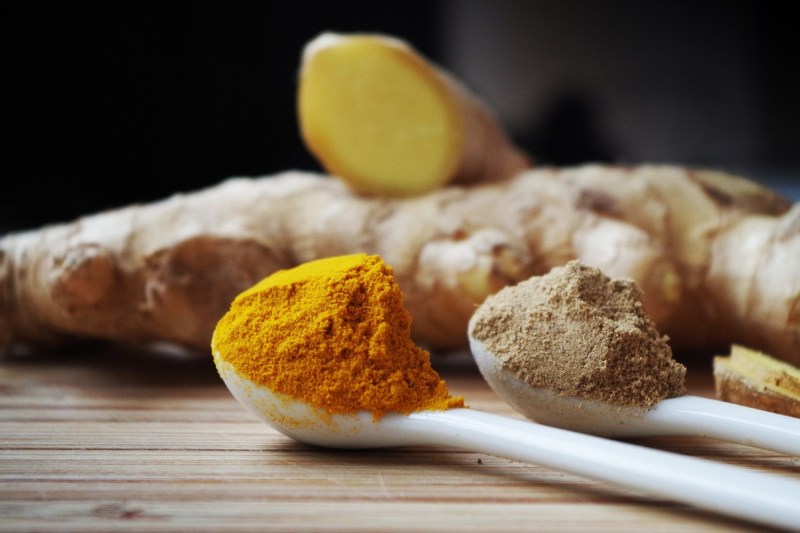

Turmeric and ginger
Numerous spices are prized for their health-promoting effects, many of which are attributed to their anti-inflammatory properties. Turmeric and ginger are often used in traditional herbal medicinal remedies to alleviate a variety of symptoms and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Turmeric contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound shown to effectively reduce joint pain and inflammation in arthritis. Studies have demonstrated that curvilinear supplementation lowers levels of C-reactive protein, a marker of systemic inflammation.
Ginger may be better known to alleviate nausea and indigestion, but it also has antibacterial and antioxidant properties that together make it an effective anti-inflammatory food. Both turmeric and ginger are roots that can be grated or juiced and eaten fresh, cooked down, steeped in teas, or used as dried spice powders to flavor all sorts of dishes.

Avocados
If you resisted the avocado toast craze, perhaps it’s time to jump on the bandwagon or consider adding avocado to salads, sandwiches, omelets, or burgers, or enjoying guacamole as a go-to condiment of choice. Avocados are packed with heart-healthy monounsaturated fats, and nutrients such as fiber, magnesium, and potassium, which help hydrate and nourish cells and cell membranes to prevent premature cell death and prevent triggering the immune system for cellular cleanup. Avocados are also high in carotenoids and tocopherols, which have been found to reduce markers of inflammation and lower the risk of certain cancers.
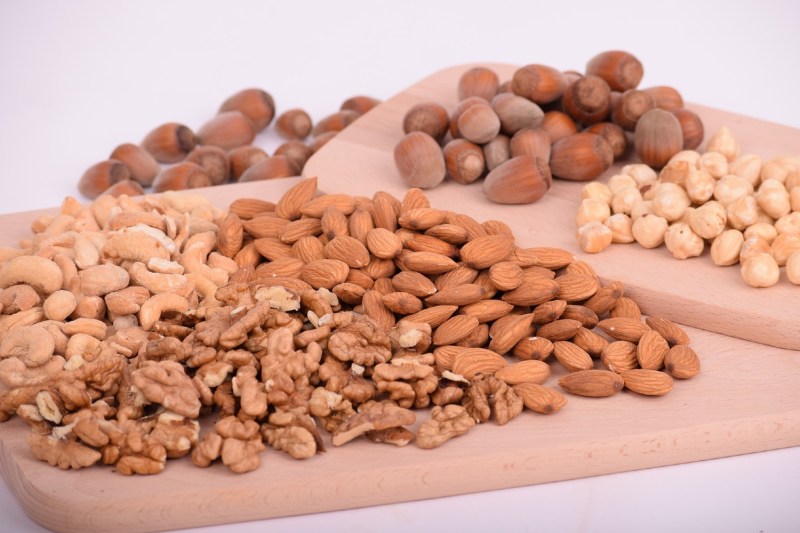

Almonds, walnuts, and other nuts
Nuts are not only rich in polyunsaturated fats, but they also are a good source of vitamin E. Vitamin E reduces inflammation in the body because it acts as a free radical scavenger, helping prevent oxidative damage and subsequent inflammatory sequelae. Vitamin E also plays a key role in several immune pathways, and a more robust immune system is better able to counter inflammation before it becomes widespread or chronic.
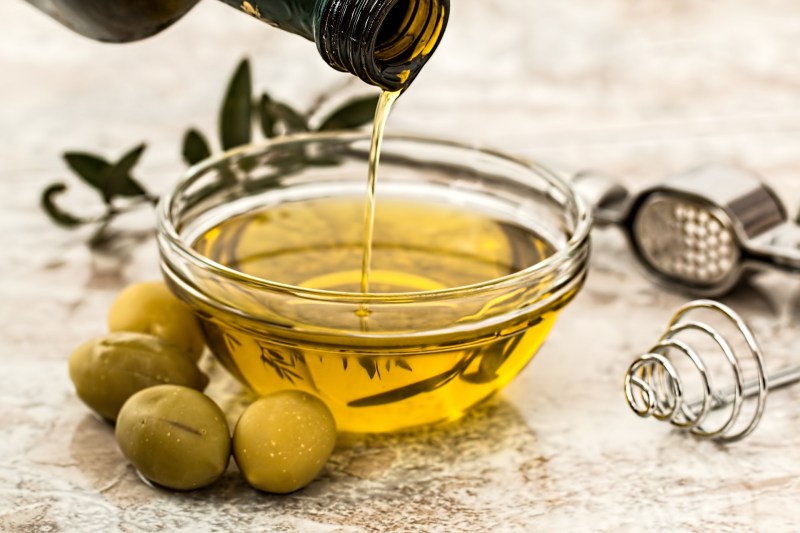

Olive oil
Olives and olive oil are rich in anti-inflammatory polyunsaturated fats. They are also a good source of the antioxidant oleocanthal, which possesses strong anti-inflammatory properties. In fact, many experts attribute the well-known disease-reducing benefits of the Mediterranean Diet to its ability to reduce systemic inflammation due to the high intake of the anti-inflammatory fats and antioxidants in olives and olive oil, which are staples in the diet.
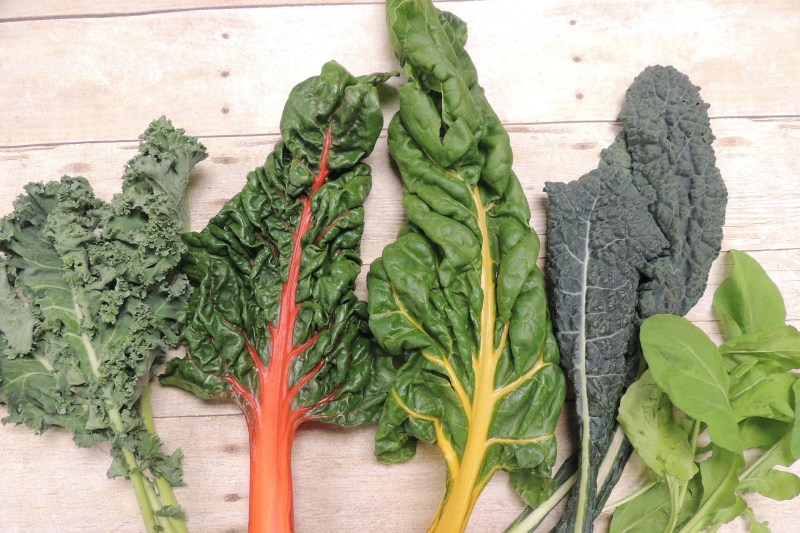

Dark, leafy greens
Dark, leafy green vegetables such as spinach, chard, kale, bok choy, and chicory contain bountiful antioxidants and vitamins, including vitamins A, C, and the B complex. They also contain water and fiber to aid digestion and many of the prebiotics most loved by gut bacteria, promoting a robust microbiome, gastric motility, and mucosal barrier function.
With a rich phytonutrient and micronutrient profile, including folate, lutein, zeaxanthin, chlorophyll, vitamin K, magnesium, potassium, and dietary nitrates, dark leafy greens are one of nature’s most effective anti-inflammatory foods. They help improve circulation by dilating blood vessels and reducing oxidative damage in the body.

Broccoli
Broccoli is often thought of as the king of healthy vegetables and when it comes to reducing inflammation, that title is rather appropriate. Like other green vegetables, broccoli is rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, which support the immune system and protect against cellular damage.
Additionally, broccoli and other cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower and Brussels sprouts contain sulforaphane, an antioxidant that inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines and necrosis factors. By reducing the concentration of these inflammatory factors, broccoli helps keep inflammation in check.

Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate and cocoa contain flavonols such as catechin that inhibit inflammation and may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attacks, and strokes. To best capitalize on the nutritious benefits of cocoa, choose dark chocolate varieties that are at least 70% cocoa — the darker the better.
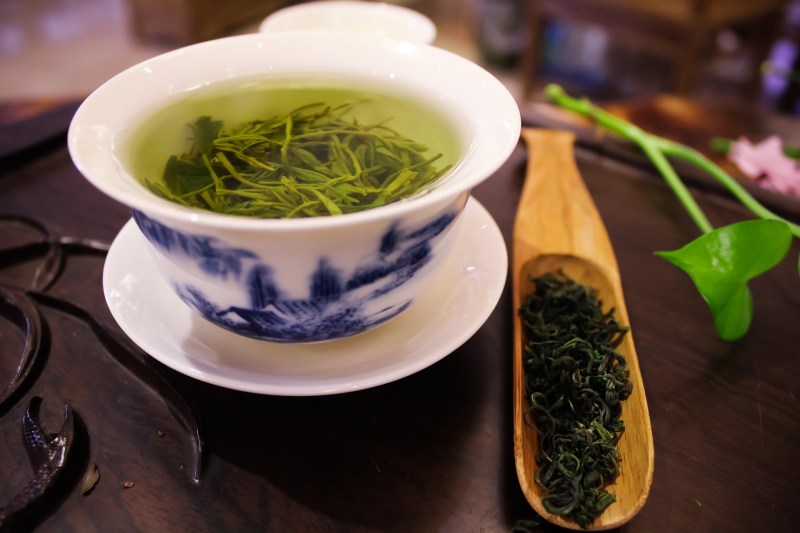

Green tea
Green tea is touted for its health benefits and has been shown to provide numerous health benefits ranging from reducing the risk of cancer and other diseases to improving memory and increasing metabolism. Many of the benefits of green tea are due to the antioxidants and polyphenols it contains, which reduce inflammation in the body and support the immune system and cellular health.
A particular potent anti-inflammatory compound in green tea is epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), which helps protect the fatty acids in your cells from oxidative damage and inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.

Coconut oil
Delicious and versatile, coconut oil is one of the easiest oils to cook with and offers great anti-inflammatory properties. In fact, some people even use it topically to help reduce skin inflammation. One study in India found that the antioxidants found in virgin coconut oil can help reduce inflammation from the inside, helping reduce symptoms of conditions such as arthritis. In the gastrointestinal system, coconut oil can also help destroy bad bacteria, a common cause of gut inflammation. Coconut oil can be used as a cooking oil for medium-to-high heat and can also be used in baking.
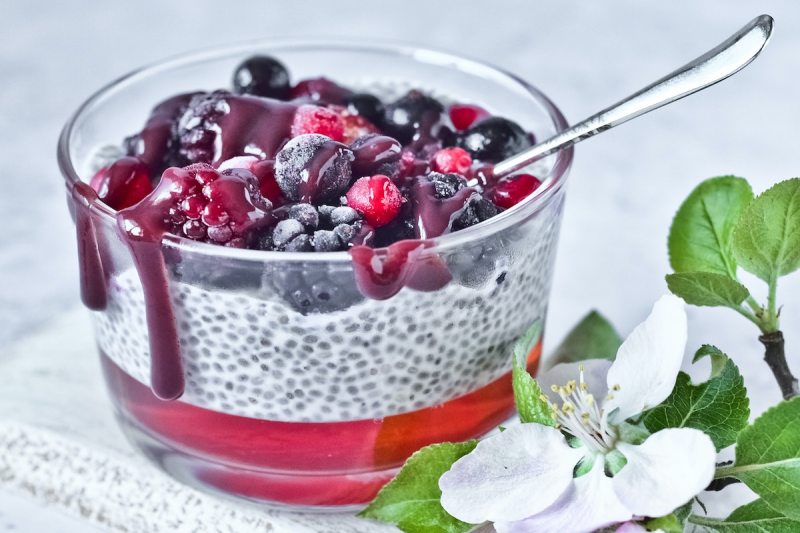

Chia seeds
Known as a popular superfood, chia seeds contain an antioxidant called caffeic acid. This antioxidant compound can be helpful for those with inflammatory health conditions and autoimmune diseases. In addition to their high levels of caffeic acid, chia seeds contain lots of alpha-linolenic acid, or ALA, a powerful omega-3 fatty acid.
Consuming chia seeds with lots of omega-3s can help balance out the harmful effects of too many omega-6s, often found in the standard American diet. Studies have shown that maintaining a good ratio of omega-6 to omega-3s can help reduce your risk of developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease.
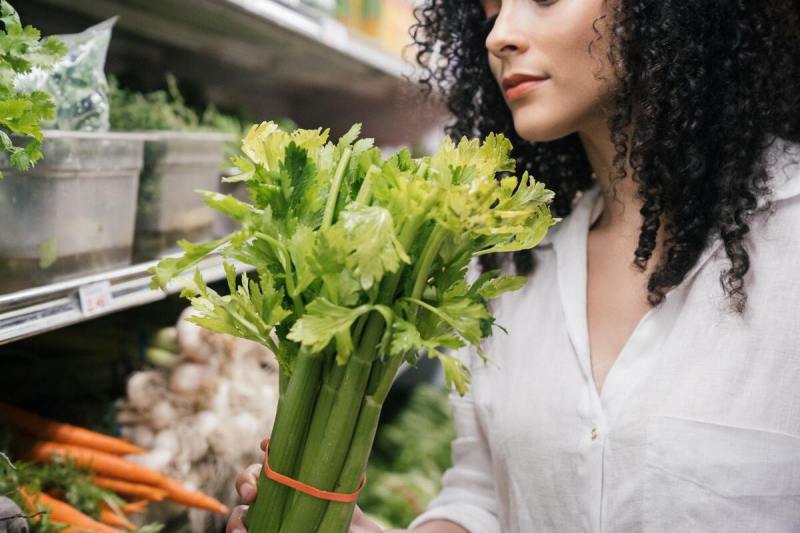

Celery
Another unique food to help fight inflammation is celery, which contains a plant compound called apigenin. This compound is often used in traditional Chinese medicine practices, as it contains anti-inflammatory properties. Not only does celery make a delicious and nutritious snack, but it may also be worth incorporating to help reduce symptoms associated with chronic inflammation.
As an added benefit, celery is also high in vitamin A, which can help support a healthy immune system, and is high in healthy fiber, too. Since celery is made up of almost 95% water, it’s considered a negative-calorie food, too, which means it’s a great weight loss food to incorporate into your diet as well.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to lose belly fat: Thanksgiving food swaps that won’t derail your fitness goals
- This one simple healthy food trick may get you to eat better more often
- How to lose belly fat: Eating these 10 foods more often will help a lot
- The 5 worst foods for bodybuilding, according to a doctor
- Chia seeds, cranberries, flaxseed & more: Report highlights why you need to be careful when eating some superfoods